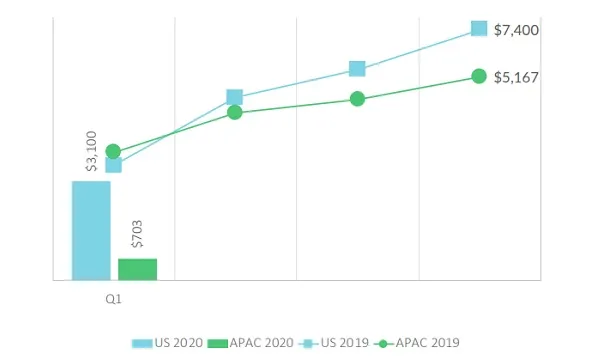
Asia-Pacific healthtech funding plunged 56% to $703m in Q1
Half of the clusters that outperformed the ecosystem were relevant to addressing COVID-19.
Asia-Pacific's healthtech funding dropped 56% YoY to $703m across 68 deals in Q1 2020, according to data from Galen Growth Asia.
China was the hardest hit, where funding plunged 78% during the quarter. Meanwhile, deal value in India soared 3.35 times, whilst South Korea and Japan accounted for 41% of all deals by volume, surging 43% YoY.
The average deal value slipped by 31% to $10.6m, no thanks to a global downward trend in valuations
"Unlike the USA, the reality of the pandemic struck Asia in January, which implemented measures earlier and significantly impacted its digital health funding momentum," the report noted.
Three of the six clusters that outperformed the ecosystem were relevant to addressing COVID-19. In particular, telemedicine recorded the biggest YoY deal value increase, skyrocketing 8.5 times. Deal value in patient solutions firms rose 18%, whilst funding for medical diagnostics fell 42%.
The quarter saw a total of two mega deals, or deals valued over $100m, in the region: one in China and one in India. This represented 36% of all funding, 4% lower compared to that of Q1 2019. Excluding mega deals, total funding value crashed 53%.
Initial public offering (IPO) and mergers and acquisition (M&A) activities accounted for a
total volume share of 6%, dipping 4% YoY. These exits include three M&A and one IPO, compared to six M&A and four IPO deals recorded in Q1 2019.
Meanwhile, the share of late-stage deals in the region surged 2.5 times to 10%. The proportion of growth-stage investments climbed 2% to 53% of the total, whilst early-stage deals shrank 15% to 29% of the total.
A third of all deals in the quarter targeted disease agnostic ventures, which also recorded the highest dollar total, closing above $230m. Investments into disease-specific solutions focused primarily on chronic diseases (17% for cardiovascular conditions and diabetes), oncology (11%), and preventive health (8%).
















 Advertise
Advertise







